Copyright 2024 All rights reserved.
What We Do
By overcoming barriers that seemed impossible, we have established platform
technologies for development of pharmaceuticals that anyone can safely use regardless of time and place.
Extracellular Vesicle Therapeutics
What is Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) ?
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are nano-sized particles limited by lipid bilayers that are released from most cells. EVs perform various biological functions such as repair and regeneration of damaged tissues, generation of new blood vessels, regulation of immune responses, and maintenance of homeostasis by delivering various substances such as proteins, mRNAs, and miRNAs contained inside to other cells or tissues. EVs are mainly used for diagnosis of diseases (especially cancer cell-derived EVs), treatment of diseases, and delivery of drugs for treatment. In particular, stem cell-derived EVs are receiving a lot of attention as candidates for next-generation advanced biopharmaceuticals that can replace stem cell treatments.
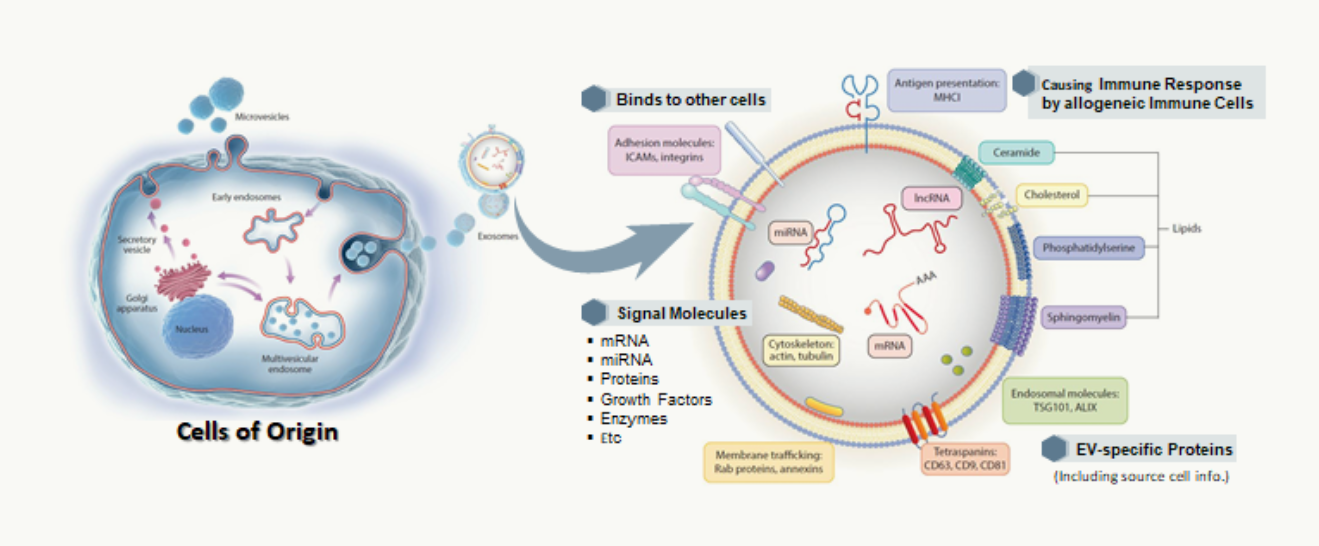
Application of Extracellular Vesicles
According to Cell Origin
Cancer Cell
- Establishing tumor
microenvironment (TME) - Promoting cancer metastasis
Immune Cells
- Delivering antigenic peptides
- Regulating immune responses
Cancer Cell
- Restore damaged cell/tissue
- Cell proliferation/differentiation
Drug delivery
Function of extracellular vesicles derived from stem cells
Alternative to
Stem Cell Therapy
-
 Regenerative treatment
Regenerative treatment
for skin, muscle, bone,
cartilage, blood vessel,
lung, kidney, heart, etc -
 Neurodegenerative disease
Neurodegenerative disease
treatment including
Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s
disease, etc -
 Autoimmune disease
Autoimmune disease
treatment
for
Atopy, asthma,
Crohn’s disease, etc -
 Anti-tumor
Anti-tumor
treatment -
 Infectious disease
Infectious disease
prevention & treatment
including COVID-19
R&D Status of
extracellular vesicle
therapeutics by diseases
(Clinical trials in progress)

Immune Rejection of EVs by mismatching MHC
Like cells, since EVs express antigenic molecules (MHC) in the lipid bilayer membrane, immune rejection by MHC-mismatching may occur when allogeneic EVs are administered. Furthermore, the proliferation of T cells is activated by the administered allogeneic EVs, which may cause undesired immune or allergic reactions. To reduce the risk of immune response by allogeneic EV therapeutics, it is recommended to match HLA-typing between donors and patients or to use immunosuppressive agents.
(Report on therapeutic preparations using extracellular vesicles (EV) including exosomes, 2023, PMDA, Japan)
Immune Rejection of allogeneic Extracellular Vesicles
Caused by Mismatching
Major Histocompatibility
Complex (MHC)
-
Cellular Uptake of
injected EVs by Phagocytosis
(macrophage and monocyte)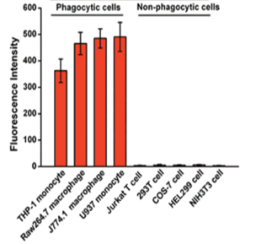 (Traffic. 2010, 11, 675)
(Traffic. 2010, 11, 675)
-
Half-life of injected EVs in blood is
about 2 mins and found
only in Lung and Spleen after 4 hr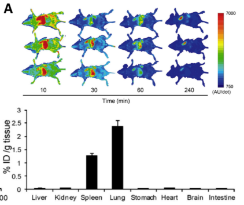 (Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1249)
(Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1249)
-
Injected EVs activate
T cell proliferation(immune response)
in concentration-dependent manner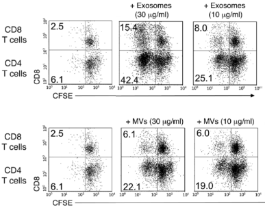 (J. Clin. Invest. 2016, 126, 2805)
(J. Clin. Invest. 2016, 126, 2805)
MBTC-EVs
World-first HLA-G+ Extracellular Vesicles Therapeutics without Immunogenicity
Ready-made EV therapeutics
safe for allogeneic application
| Item | HLA-G+ MBTC-EVs | HLA-G- EVs (from ESCs, iPSCs, MSCs, HSCs) |
|---|---|---|
| Expression of HLA-A/B/C | Yes | Yes |
| Expression and Secretion of HLA-G | Yes | No |
| Immunogenicity | No | Yes |
| Possible for allogeneic use | Yes | No |
| Need to match HLA-typing | No | Yes |
| Need to use immunosuppressant | No | Yes |